from PIL import ImageTorch 核心
setup_cuda
setup_cuda (benchmark=True)
设置主 CUDA 设备并将 cudnn.benchmark 设置为 benchmark
数组和显示
subplots
subplots (nrows:int=1, ncols:int=1, figsize:tuple=None, imsize:int=3, suptitle:str=None, sharex:"bool|Literal['none','all','row','col']"=False, sharey:"bool|Literal['none','all','row','col']"=False, squeeze:bool=True, width_ratios:Sequence[float]|None=None, height_ratios:Sequence[float]|None=None, subplot_kw:dict[str,Any]|None=None, gridspec_kw:dict[str,Any]|None=None, **kwargs)
返回一个 Figure 和一组 Subplots,用于显示 imsize 英寸大小的图像
| 类型 | 默认值 | 详情 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| nrows | int | 1 | 返回的坐标轴网格中的行数 |
| ncols | int | 1 | 返回的坐标轴网格中的列数 |
| figsize | tuple | None | 返回的 Figure 的宽度、高度(单位:英寸) |
| imsize | int | 3 | 将在返回的 Figure 中显示的图像大小(单位:英寸) |
| suptitle | str | None | 设置给返回的 Figure 的标题 |
| sharex | bool | Literal[‘none’, ‘all’, ‘row’, ‘col’] | False | |
| sharey | bool | Literal[‘none’, ‘all’, ‘row’, ‘col’] | False | |
| squeeze | bool | True | |
| width_ratios | Sequence[float] | None | None | |
| height_ratios | Sequence[float] | None | None | |
| subplot_kw | dict[str, Any] | None | None | |
| gridspec_kw | dict[str, Any] | None | None | |
| kwargs | VAR_KEYWORD | ||
| 返回值 | (plt.Figure, plt.Axes) | 以元组形式返回 fig 和 ax |
这在 get_grid 中使用。suptitle, sharex, sharey, squeeze, subplot_kw 和 gridspec_kw 都向下传递给 plt.subplots。
show_image
show_image (im, ax=None, figsize=None, title=None, ctx=None, cmap=None, norm=None, aspect=None, interpolation=None, alpha=None, vmin=None, vmax=None, colorizer=None, origin=None, extent=None, interpolation_stage=None, filternorm=True, filterrad=4.0, resample=None, url=None, data=None, **kwargs)
在 ax 上显示一个 PIL 或 PyTorch 图像。
show_image 可以显示 PIL 图像…
im = Image.open(TEST_IMAGE_BW)
ax = show_image(im, cmap="Greys")
…以及具有标准 CHW 维度顺序的彩色图像…
im2 = np.array(Image.open(TEST_IMAGE))
ax = show_image(im2, figsize=(2,2))
…以及具有 HWC 维度顺序的彩色图像…
im3 = torch.as_tensor(im2).permute(2,0,1)
ax = show_image(im3, figsize=(2,2))
show_titled_image
show_titled_image (o, ax=None, figsize=None, title=None, ctx=None, cmap=None, norm=None, aspect=None, interpolation=None, alpha=None, vmin=None, vmax=None, colorizer=None, origin=None, extent=None, interpolation_stage=None, filternorm=True, filterrad=4.0, resample=None, url=None, data=None, **kwargs)
调用 show_image 并将 o 解构为 (img,title)
show_titled_image((im3,'A puppy'), figsize=(2,2))
使用 titles 将所有图像 ims 显示为具有 rows 的子图。suptitle 提供了一种为所有图像创建 Figure 标题的方法。如果使用 suptitle,则除非将 constrained_layout 设置为 False,否则会使用 constrained_layout。
show_images
show_images (ims, nrows=1, ncols=None, titles=None, figsize:tuple=None, imsize:int=3, suptitle:str=None, sharex:"bool|Literal['none','all','row','col']"=False, sharey:"bool|Literal['none','all','row','col']"=False, squeeze:bool=True, width_ratios:Sequence[float]|None=None, height_ratios:Sequence[float]|None=None, subplot_kw:dict[str,Any]|None=None, gridspec_kw:dict[str,Any]|None=None)
使用 titles 将所有图像 ims 显示为具有 rows 的子图。
| 类型 | 默认值 | 详情 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ims | |||
| nrows | int | 1 | 返回的坐标轴网格中的行数 |
| ncols | int | 1 | 返回的坐标轴网格中的列数 |
| titles | NoneType | None | |
| figsize | tuple | None | 返回的 Figure 的宽度、高度(单位:英寸) |
| imsize | int | 3 | 将在返回的 Figure 中显示的图像大小(单位:英寸) |
| suptitle | str | None | 设置给返回的 Figure 的标题 |
| sharex | bool | Literal[‘none’, ‘all’, ‘row’, ‘col’] | False | |
| sharey | bool | Literal[‘none’, ‘all’, ‘row’, ‘col’] | False | |
| squeeze | bool | True | |
| width_ratios | Sequence[float] | None | None | |
| height_ratios | Sequence[float] | None | None | |
| subplot_kw | dict[str, Any] | None | None | |
| gridspec_kw | dict[str, Any] | None | None | |
| 返回值 | (plt.Figure, plt.Axes) | 以元组形式返回 fig 和 ax |
show_images((im,im3),titles=('number','puppy'),suptitle='Number Puppy', imsize=3)
ArrayImage, ArrayImageBW 和 ArrayMask 是 ndarray 的子类,它们知道如何显示自身。
ArrayBase
一个可以修改类型转换行为的 ndarray
ArrayImageBase
表示图像的数组基类
ArrayImage
表示图像的数组
ArrayImageBW
表示图像的数组
ArrayMask
表示图像掩码的数组
im = Image.open(TEST_IMAGE)im_t = cast(im, ArrayImage)
test_eq(type(im_t), ArrayImage)ax = im_t.show(figsize=(2,2))
test_fig_exists(ax)基础
Tensor.__array_eq__
Tensor.__array_eq__ (b)
tensor
tensor (x, *rest, dtype=None, device=None, requires_grad=False, pin_memory=False)
与 torch.as_tensor 类似,但也处理列表,并且可以直接传递多个向量元素。
test_eq(tensor(torch.tensor([1,2,3])), torch.tensor([1,2,3]))
test_eq(tensor(array([1,2,3])), torch.tensor([1,2,3]))
test_eq(tensor(1,2,3), torch.tensor([1,2,3]))
test_eq_type(tensor(1.0), torch.tensor(1.0))set_seed 对于跨运行重现结果非常有用。重要的是要记住,某些类(例如 Dataloaders)具有不受此函数影响的内部随机数生成器,因此必须在此类对象创建之前运行此函数以确保可重现性。
set_seed
set_seed (s, reproducible=False)
为 random、torch 和 numpy(如果可用)设置随机种子
这是 set_seed 如何用于重置随机数生成器状态的示例。
set_seed(2*33)
a1 = np.random.random()
a2 = torch.rand(())
a3 = random.random()
set_seed(2*33)
b1 = np.random.random()
b2 = torch.rand(())
b3 = random.random()
print('a\'s: {0:3.3f} {1:3.3f} {2:3.3f}'.format(a1,a2,a3))
print('b\'s: {0:3.3f} {1:3.3f} {2:3.3f}'.format(b1,b2,a3))a's: 0.154 0.498 0.071
b's: 0.154 0.498 0.071test_eq(a1,b1)
test_eq(a2,b2)
test_eq(a3,b3)get_random_states 和 set_random_states 对于存储状态以便稍后可以返回非常有用。
get_random_states
get_random_states ()
获取 random、torch 和 numpy 随机数生成器的状态
set_random_states
set_random_states (random_state, numpy_state, torch_state, torch_cuda_state, torch_deterministic, torch_benchmark)
设置 random、torch 和 numpy 随机数生成器的状态
请注意,下面的旧值和回滚值是相同的,因为我们能够返回到先前的状态。
old_states = get_random_states()
olds = (random.random(),np.random.random(),torch.rand(()))
news = (random.random(),np.random.random(),torch.rand(()))
set_random_states(**old_states)
rewinds = (random.random(),np.random.random(),torch.rand(()))
print('olds: {0:3.3f} {1:3.3f} {2:3.3f}'.format(*olds))
print('news: {0:3.3f} {1:3.3f} {2:3.3f}'.format(*news))
print('rewinds: {0:3.3f} {1:3.3f} {2:3.3f}'.format(*rewinds))olds: 0.435 0.134 0.023
news: 0.246 0.363 0.227
rewinds: 0.435 0.134 0.023test_ne(olds,news)
test_eq(olds,rewinds)在 no_random 中,我们将使用 get_random_states 和 set_random_states 回滚状态的想法与使用 set_seed 的能力结合起来,并创建一个上下文管理器,允许我们在部分代码中控制随机性。
注意:类似于 torch.random.fork_rng,但也包括 numpy 和 random
no_random
no_random (seed=42, reproducible=True)
存储和检索随机数生成器的状态。为 random、torch 和 numpy 设置随机种子。
这里有一些关于如何使用 no_random 来控制代码块内随机性的示例。
states=get_random_states()
olds = (random.random(),np.random.random(),torch.rand(()))
set_random_states(**states) #rewinding above random calls
with no_random():
new1 = (random.random(),np.random.random(),torch.rand(()))
with no_random():
new2 = (random.random(),np.random.random(),torch.rand(()))
with no_random(seed=100):
seeded1 = (random.random(),np.random.random(),torch.rand(()))
with no_random(seed=100):
seeded2 = (random.random(),np.random.random(),torch.rand(()))
rewinds = (random.random(),np.random.random(),torch.rand(()))
print('olds: {0:3.3f} {1:3.3f} {2:3.3f}'.format(*olds))
print('new1: {0:3.3f} {1:3.3f} {2:3.3f}'.format(*new1))
print('new2: {0:3.3f} {1:3.3f} {2:3.3f}'.format(*new2))
print('seeded1: {0:3.3f} {1:3.3f} {2:3.3f}'.format(*seeded1))
print('seeded2: {0:3.3f} {1:3.3f} {2:3.3f}'.format(*seeded2))
print('rewinds: {0:3.3f} {1:3.3f} {2:3.3f}'.format(*rewinds))olds: 0.246 0.363 0.227
new1: 0.639 0.375 0.882
new2: 0.639 0.375 0.882
seeded1: 0.146 0.543 0.112
seeded2: 0.146 0.543 0.112
rewinds: 0.246 0.363 0.227请注意,olds 和 rewinds 也彼此相等。由此我们可以看到,with 块中的所有内容都没有更新块外的状态。在块内部,对于任何特定的种子,状态都会被重置,因此对于相同的种子,您应该获得相同的随机数生成器结果。
注意:重要的是要记住,像 Dataloader 这样的类具有内部随机数生成器,并且 no_random 对这些随机数生成器没有影响。
test_ne(olds,new1)
test_eq(new1,new2)
test_ne(new1,seeded1)
test_eq(seeded1,seeded2)
test_eq(olds,rewinds)unsqueeze
unsqueeze (x, dim=-1, n=1)
与 torch.unsqueeze 相同,但可以添加 n 个维度
t = tensor([1])
t2 = unsqueeze(t, n=2)
test_eq(t2,t[:,None,None])unsqueeze_
unsqueeze_ (x, dim=-1, n=1)
与 torch.unsqueeze_ 相同,但可以添加 n 个维度
t = tensor([1])
unsqueeze_(t, n=2)
test_eq(t, tensor([1]).view(1,1,1))apply
apply (func, x, *args, **kwargs)
递归地将 func 应用于 x,并传递参数
maybe_gather
maybe_gather (x, axis=0)
在分布式训练时,在 axis 上收集 x 的副本
to_detach
to_detach (b, cpu=True, gather=True)
递归地分离 b 中张量列表;如果 cpu=True,则将其放在 CPU 上。
gather 仅在分布式训练期间应用,如果 gather=True,结果张量将是跨进程收集的张量(因此,批大小将乘以进程数)。
to_half
to_half (b)
递归地将 b 中的浮点张量映射到 FP16。
to_float
to_float (b)
递归地将 b 中的浮点张量映射到 float。
default_device
default_device (use=-1)
返回或设置默认设备;use_cuda: -1 - 如果可用,则使用 CUDA/mps;True - 如果不可用,则报错;False - CPU
if torch.cuda.is_available():
_td = torch.device(torch.cuda.current_device())
test_eq(default_device(-1), _td)
test_eq(default_device(True), _td)
else:
test_eq(default_device(False), torch.device('cpu'))
default_device(-1);to_device
to_device (b, device=None, non_blocking=False)
递归地将 b 放在 device 上。
t = to_device((3,(tensor(3),tensor(2))))
t1,(t2,t3) = tif torch.cuda.is_available():
test_eq_type(t,(3,(tensor(3).cuda(),tensor(2).cuda())))
test_eq(t2.type(), "torch.cuda.LongTensor")
test_eq(t3.type(), "torch.cuda.LongTensor")to_cpu
to_cpu (b)
递归地将 b 中的张量映射到 CPU。
t3 = to_cpu(t3)
test_eq(t3.type(), "torch.LongTensor")
test_eq(t3, 2)to_np
to_np (x)
将张量转换为 numpy 数组。
t3 = to_np(t3)
test_eq(type(t3), np.ndarray)
test_eq(t3, 2)to_concat
to_concat (xs, dim=0)
连接 xs 中的元素(如果它们是元组/张量列表,则递归连接)
test_eq(to_concat([tensor([1,2]), tensor([3,4])]), tensor([1,2,3,4]))
test_eq(to_concat([tensor([[1,2]]), tensor([[3,4]])], dim=1), tensor([[1,2,3,4]]))
test_eq_type(to_concat([(tensor([1,2]), tensor([3,4])), (tensor([3,4]), tensor([5,6]))]), (tensor([1,2,3,4]), tensor([3,4,5,6])))
test_eq_type(to_concat([[tensor([1,2]), tensor([3,4])], [tensor([3,4]), tensor([5,6])]]), [tensor([1,2,3,4]), tensor([3,4,5,6])])
test_eq_type(to_concat([(tensor([1,2]),), (tensor([3,4]),)]), (tensor([1,2,3,4]),))
test_eq(to_concat([tensor([[1,2]]), tensor([[3,4], [5,6]])], dim=1), [tensor([1]),tensor([3, 5]),tensor([4, 6])])test_eq(type(to_concat([dict(foo=tensor([1,2]), bar=tensor(3,4))])), dict)Tensor 子类型
Tensor.set_meta
Tensor.set_meta (x, as_copy=False)
设置 __dict__ 中的所有元数据
Tensor.as_subclass
Tensor.as_subclass (typ)
转换为 typ 并包含 __dict__ 和 meta
Tensor.set_meta 和 Tensor.as_subclass 协同工作,在类型转换后保留 __dict__。
class _T(Tensor): pass
t = tensor(1.).requires_grad_()
t.img_size = 1
t2 = t.as_subclass(_T)
test_eq(t.img_size, t2.img_size)
test_eq(t2.img_size, 1)
assert(t2.requires_grad_)TensorBase
TensorBase (x, **kwargs)
一个支持子类序列化并在类型转换或方法调用后保留元数据的 Tensor
TensorBase 挂接到 __torch_function__ 以确保元数据不丢失。要查看所有被调用的函数,请设置 debug。
a = TensorBase(1)
TensorBase.debug=True
1/(a+1)TensorBase(0.5000)TensorBase 及其子类也允许将元数据大小作为 img_size 传递…
from torch.utils.data._utils.collate import default_collatea = TensorBase(1,img_size=(128,128))
test_eq(a.img_size,(128,128))
b = cast(a,TensorBase)
test_eq(b.img_size,(128,128))
test_eq(torch.stack([a,b],0).img_size,(128,128))
test_eq(default_collate([a,b]).img_size,(128,128))class _TImage(TensorBase): pass
class _TImage2(_TImage): pass
t1 = _TImage([1.])
t2 = _TImage2([1.])
t2+t1_TImage2([2.])class _T(TensorBase): pass
t = _T(range(5))
test_eq(t[0], 0)
test_eq_type(t+1, _T(range(1,6)))
test_eq(repr(t), '_T([0, 1, 2, 3, 4])')
test_eq_type(t[_T([False,False,True,True,True])], _T([2,3,4]))
test_eq_type(t[_T([2,3,4])], _T([2,3,4]))
test_eq(type(pickle.loads(pickle.dumps(t))), _T)
test_eq_type(t.new_ones(1), _T([1]))
test_eq_type(t.new_tensor([1,2]), _T([1,2]))t = tensor([1,2,3])
m = TensorBase([False,True,True])
test_eq(t[m], tensor([2,3]))
t = tensor([[1,2,3],[1,2,3]])
m = cast(tensor([[False,True,True],
[False,True,True]]), TensorBase)
test_eq(t[m], tensor([2,3,2,3]))t = tensor([[1,2,3],[1,2,3]])
t.img_size = 1
t2 = cast(t, TensorBase)
test_eq(t2.img_size, t.img_size)
x = retain_type(tensor([4,5,6]), t2)
test_eq(x.img_size, t.img_size)
t3 = TensorBase([[1,2,3],[1,2,3]], img_size=1)
test_eq(t3.img_size, t.img_size)
t4 = t2+1
t4.img_size = 2
test_eq(t2.img_size, 1)
test_eq(t4.img_size, 2)
# this will fail with `Tensor` but works with `TensorBase`
test_eq(pickle.loads(pickle.dumps(t2)).img_size, t2.img_size)TensorImageBase
TensorImageBase (x, **kwargs)
一个支持子类序列化并在类型转换或方法调用后保留元数据的 Tensor
TensorImage
TensorImage (x, **kwargs)
一个支持子类序列化并在类型转换或方法调用后保留元数据的 Tensor
TensorImageBW
TensorImageBW (x, **kwargs)
一个支持子类序列化并在类型转换或方法调用后保留元数据的 Tensor
TensorMask
TensorMask (x, **kwargs)
一个支持子类序列化并在类型转换或方法调用后保留元数据的 Tensor
im = Image.open(TEST_IMAGE)
im_t = cast(array(im), TensorImage)
test_eq(type(im_t), TensorImage)im_t2 = cast(tensor(1), TensorMask)
test_eq(type(im_t2), TensorMask)
test_eq(im_t2, tensor(1))
ax = im_t.show(figsize=(2,2))
_ =(im_t == im_t2)
test_fig_exists(ax)TensorMask 和 TensorImageBase 对象之间的操作返回 TensorImageBase 对象的类型
a = TensorMask([1,2])
test_eq_type(TensorImage(1)+a, TensorImage([2,3]))
test_eq_type(1-a, TensorMask([0,-1]))TensorFlowField
TensorFlowField (x, **kwargs)
一个支持子类序列化并在类型转换或方法调用后保留元数据的 Tensor
t1 = TensorImage([1.]).view(1,1,1,1)
t2 = TensorFlowField([1.,1.]).view(1,1,1,2)
test_eq_type(F.grid_sample(t1, t2), TensorImage([[[[0.25]]]]))TensorCategory
TensorCategory (x, **kwargs)
一个支持子类序列化并在类型转换或方法调用后保留元数据的 Tensor
tc = TensorCategory([1,2,3])
mask_t = TensorMask([0,2,4,5])
im_t = TensorImage([0,2,4,5])
test_eq(mask_t[tc], tensor([2,4,5]))
test_eq(im_t[tc], tensor([2,4,5]))TensorMultiCategory
TensorMultiCategory (x, **kwargs)
一个支持子类序列化并在类型转换或方法调用后保留元数据的 Tensor
TitledTensorScalar
TitledTensorScalar (x, **kwargs)
包含具有 show 方法的标量的张量
L.cat
L.cat (dim=0)
与 torch.cat 相同
L.stack
L.stack (dim=0)
与 torch.stack 相同
L.tensored
L.tensored ()
mapped(张量)
L.tensored
L.tensored ()
mapped(张量)
如果您的 L 包含张量或可转换的内容,则可以使用 torch.stack 和 torch.cat 的快捷方式。您可以使用 tensored 手动转换。
t = L(([1,2],[3,4]))
test_eq(t.tensored(), [tensor(1,2),tensor(3,4)])L.stack
L.stack (dim=0)
与 torch.stack 相同
test_eq(t.stack(), tensor([[1,2],[3,4]]))L.cat
L.cat (dim=0)
与 torch.cat 相同
test_eq(t.cat(), tensor([1,2,3,4]))块
concat
concat (*ls)
连接张量、数组、列表或元组
a,b,c = [1],[1,2],[1,1,2]
test_eq(concat(a,b), c)
test_eq_type(concat(tuple (a),tuple (b)), tuple (c))
test_eq_type(concat(array (a),array (b)), array (c))
test_eq_type(concat(tensor(a),tensor(b)), tensor(c))
test_eq_type(concat(TensorBase(a),TensorBase(b)), TensorBase(c))
test_eq_type(concat([1,1],1), [1,1,1])
test_eq_type(concat(1,1,1), L(1,1,1))
test_eq_type(concat(L(1,2),1), L(1,2,1))块
Chunks (chunks, lens=None)
对列表的列表进行切片和整数索引
docs = L(list(string.ascii_lowercase[a:b]) for a,b in ((0,3),(3,7),(7,8),(8,16),(16,24),(24,26)))
b = Chunks(docs)
test_eq([b[ o] for o in range(0,5)], ['a','b','c','d','e'])
test_eq([b[-o] for o in range(1,6)], ['z','y','x','w','v'])
test_eq(b[6:13], 'g,h,i,j,k,l,m'.split(','))
test_eq(b[20:77], 'u,v,w,x,y,z'.split(','))
test_eq(b[:5], 'a,b,c,d,e'.split(','))
test_eq(b[:2], 'a,b'.split(','))t = torch.arange(26)
docs = L(t[a:b] for a,b in ((0,3),(3,7),(7,8),(8,16),(16,24),(24,26)))
b = Chunks(docs)
test_eq([b[ o] for o in range(0,5)], range(0,5))
test_eq([b[-o] for o in range(1,6)], [25,24,23,22,21])
test_eq(b[6:13], torch.arange(6,13))
test_eq(b[20:77], torch.arange(20,26))
test_eq(b[:5], torch.arange(5))
test_eq(b[:2], torch.arange(2))docs = L(TensorBase(t[a:b]) for a,b in ((0,3),(3,7),(7,8),(8,16),(16,24),(24,26)))
b = Chunks(docs)
test_eq_type(b[:2], TensorBase(range(2)))
test_eq_type(b[:5], TensorBase(range(5)))
test_eq_type(b[9:13], TensorBase(range(9,13)))简单类型
show_title
show_title (o, ax=None, ctx=None, label=None, color='black', **kwargs)
将 ax 的标题设置为 o,如果 ax 为 None,则打印 o
test_stdout(lambda: show_title("title"), "title")
# ensure that col names are unique when showing to a pandas series
assert show_title("title", ctx=pd.Series(dict(a=1)), label='a').equals(pd.Series(dict(a=1,a_='title')))ShowTitle
ShowTitle ()
添加简单 show 方法的基类
TitledInt
具有 show 方法的 int
TitledStr
具有 show 方法的 str
TitledFloat
TitledFloat (x=0)
具有 show 方法的 float
test_stdout(lambda: TitledStr('s').show(), 's')
test_stdout(lambda: TitledInt(1).show(), '1')TitledTuple
TitledTuple (x=None, *rest)
具有 show 方法的 fastuple
TitledStr.truncate
TitledStr.truncate (n)
将自身截断为 n
其他函数
DataFrame.__init__
DataFrame.__init__ (data=None, index=None, columns=None, dtype=None, copy=None)
get_empty_df
get_empty_df (n)
返回数据框的 n 个空行
display_df
display_df (df)
在 notebook 中显示 df 或默认打印
get_first
get_first (c)
获取 c 的第一个元素,即使 c 是一个数据框
one_param
one_param (m)
m 中的第一个参数
item_find
item_find (x, idx=0)
递归地获取 x 的第 idx 个元素
find_device
find_device (b)
递归地搜索 b 的设备。
t2 = to_device(tensor(0))
dev = default_device()
test_eq(find_device(t2), dev)
test_eq(find_device([t2,t2]), dev)
test_eq(find_device({'a':t2,'b':t2}), dev)
test_eq(find_device({'a':[[t2],[t2]],'b':t2}), dev)find_bs
find_bs (b)
递归地搜索 b 的批大小。
x = torch.randn(4,5)
x1 = [1,2,3]
test_eq(find_bs(x1), 3)
test_eq(find_bs(x), 4)
test_eq(find_bs((x,x)), 4)
test_eq(find_bs([x, x]), 4)
test_eq(find_bs({'a':x,'b':x}), 4)
test_eq(find_bs({'a':[[x],[x]],'b':x}), 4)np_func
np_func (f)
将接受和返回 numpy 数组的函数转换为接受和返回张量的函数
这个装饰器对于例如将 numpy 函数用作 fastai 指标特别有用
from sklearn.metrics import f1_score@np_func
def f1(inp,targ): return f1_score(targ, inp)
a1,a2 = array([0,1,1]),array([1,0,1])
t = f1(tensor(a1),tensor(a2))
test_eq(f1_score(a1,a2), t)
assert isinstance(t,Tensor)Module
Module ()
与 nn.Module 相同,但子类无需调用 super().__init__
class _T(Module):
def __init__(self): self.f = nn.Linear(1,1)
def forward(self,x): return self.f(x)
t = _T()
t(tensor([1.]))tensor([-0.0832], grad_fn=<AddBackward0>)get_model
get_model (model)
返回可能包装在 model 内部的模型。
one_hot
one_hot (x, c)
对具有 c 个类别的 x 进行独热编码。
test_eq(one_hot([1,4], 5), tensor(0,1,0,0,1).byte())
test_eq(one_hot(torch.tensor([]), 5), tensor(0,0,0,0,0).byte())
test_eq(one_hot(2, 5), tensor(0,0,1,0,0).byte())one_hot_decode
one_hot_decode (x, vocab=None)
test_eq(one_hot_decode(tensor(0,1,0,0,1)), [1,4])
test_eq(one_hot_decode(tensor(0,0,0,0,0)), [ ])
test_eq(one_hot_decode(tensor(0,0,1,0,0)), [2 ])params
params (m)
返回 m 的所有参数
trainable_params
trainable_params (m)
返回 m 的所有可训练参数
m = nn.Linear(4,5)
test_eq(trainable_params(m), [m.weight, m.bias])
m.weight.requires_grad_(False)
test_eq(trainable_params(m), [m.bias])norm_bias_params
norm_bias_params (m, with_bias=True)
返回所有偏置和 BatchNorm 参数
for norm_func in [nn.BatchNorm1d, partial(nn.InstanceNorm1d, affine=True)]:
model = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(10,20), norm_func(20), nn.Conv1d(3,4, 3))
test_eq(norm_bias_params(model), [model[0].bias, model[1].weight, model[1].bias, model[2].bias])
model = nn.ModuleList([nn.Linear(10,20, bias=False), nn.Sequential(norm_func(20), nn.Conv1d(3,4,3))])
test_eq(norm_bias_params(model), [model[1][0].weight, model[1][0].bias, model[1][1].bias])
model = nn.ModuleList([nn.Linear(10,20), nn.Sequential(norm_func(20), nn.Conv1d(3,4,3))])
test_eq(norm_bias_params(model, with_bias=False), [model[1][0].weight, model[1][0].bias])batch_to_samples
batch_to_samples (b, max_n=10)
将一个批次“转置”为(最多 max_n)个样本
t = tensor([1,2,3])
test_eq(batch_to_samples([t,t+1], max_n=2), ([1,2],[2,3]))
test_eq(batch_to_samples(tensor([1,2,3]), 10), [1, 2, 3])
test_eq(batch_to_samples([tensor([1,2,3]), tensor([4,5,6])], 10), [(1, 4), (2, 5), (3, 6)])
test_eq(batch_to_samples([tensor([1,2,3]), tensor([4,5,6])], 2), [(1, 4), (2, 5)])
test_eq(batch_to_samples([tensor([1,2,3]), [tensor([4,5,6]),tensor([7,8,9])]], 10),
[(1, (4, 7)), (2, (5, 8)), (3, (6, 9))])
test_eq(batch_to_samples([tensor([1,2,3]), [tensor([4,5,6]),tensor([7,8,9])]], 2), [(1, (4, 7)), (2, (5, 8))])
t = fastuple(tensor([1,2,3]),TensorBase([2,3,4]))
test_eq_type(batch_to_samples(t)[0][1], TensorBase(2))
test_eq(batch_to_samples(t).map(type), [fastuple]*3)Tensor.interp_1d
Tensor.interp_1d (x:torch.Tensor, xp, fp)
与 np.interp 相同
brks = tensor(0,1,2,4,8,64).float()
ys = tensor(range_of(brks)).float()
ys /= ys[-1].item()
pts = tensor(0.2,0.5,0.8,3,5,63)
preds = pts.interp_1d(brks, ys)
test_close(preds.numpy(), np.interp(pts.numpy(), brks.numpy(), ys.numpy()))
plt.scatter(brks,ys)
plt.scatter(pts,preds)
plt.legend(['breaks','preds']);
Tensor.pca
Tensor.pca (x:torch.Tensor, k=2)
计算 x 的 PCA,维度为 k。
logit
logit (x)
x 的 Logit,钳位以避免无穷大。
num_distrib
num_distrib ()
返回分布式训练中的进程数(如果适用)。
rank_distrib
rank_distrib ()
返回此进程的分布式 rank(如果适用)。
distrib_barrier
distrib_barrier ()
在分布式训练中设置同步屏障
调用此函数后,PyTorch 进程组中的所有子进程都必须到达此处才能继续。
Path.save_array
Path.save_array (p:pathlib.Path, o, complib='lz4', lvl=3)
使用压缩级别 lvl 将 numpy 数组保存到压缩的 pytables 文件
压缩库可以是以下任何一种:blosclz, lz4, lz4hc, snappy, zlib 或 zstd。
Path.load_array
Path.load_array (p:pathlib.Path)
将 numpy 数组保存到 pytables 文件
base_doc
base_doc (elt)
打印 elt 的基本文档
doc
doc (elt)
尝试使用 nbdev 中的文档,如果失败则回退到 base_doc
nested_reorder
nested_reorder (t, idxs)
使用 idxs 对 t 中的所有张量重新排序
x = tensor([0,1,2,3,4,5])
idxs = tensor([2,5,1,0,3,4])
test_eq_type(nested_reorder(([x], x), idxs), ([idxs], idxs))
y = L(0,1,2,3,4,5)
z = L(i.item() for i in idxs)
test_eq_type(nested_reorder((y, x), idxs), (z,idxs))flatten_check
flatten_check (inp, targ)
检查 inp 和 targ 具有相同的元素数量并将其展平。
x1,x2 = torch.randn(5,4),torch.randn(20)
x1,x2 = flatten_check(x1,x2)
test_eq(x1.shape, [20])
test_eq(x2.shape, [20])
x1,x2 = torch.randn(5,4),torch.randn(21)
test_fail(lambda: flatten_check(x1,x2))图像辅助函数
make_cross_image
make_cross_image (bw=True)
创建一个包含交叉图像的张量,可以是 bw (True) 或彩色
plt.imshow(make_cross_image(), cmap="Greys");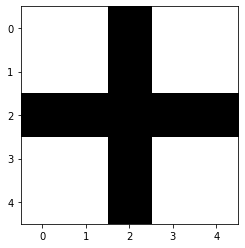
plt.imshow(make_cross_image(False).permute(1,2,0));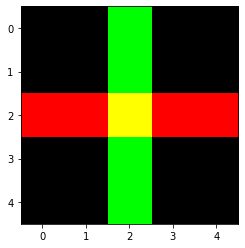
show_image_batch
show_image_batch (b, show=<function show_titled_image>, items=9, cols=3, figsize=None, **kwargs)
以 cols 列宽度的 items 大小网格显示批次 b
show_image_batch(([Image.open(TEST_IMAGE_BW),Image.open(TEST_IMAGE)],['bw','color']), items=2)
模型初始化
requires_grad
requires_grad (m)
检查 m 的第一个参数是否需要梯度
tst = nn.Linear(4,5)
assert requires_grad(tst)
for p in tst.parameters(): p.requires_grad_(False)
assert not requires_grad(tst)init_default
init_default (m, func=<function kaiming_normal_>)
使用 func 初始化 m 的权重并将 bias 设置为 0。
tst = nn.Linear(4,5)
tst.weight.data.uniform_(-1,1)
tst.bias.data.uniform_(-1,1)
tst = init_default(tst, func = lambda x: x.data.fill_(1.))
test_eq(tst.weight, torch.ones(5,4))
test_eq(tst.bias, torch.zeros(5))cond_init
cond_init (m, func)
将 init_default 应用于 m,除非它是 batchnorm 模块
tst = nn.Linear(4,5)
tst.weight.data.uniform_(-1,1)
tst.bias.data.uniform_(-1,1)
cond_init(tst, func = lambda x: x.data.fill_(1.))
test_eq(tst.weight, torch.ones(5,4))
test_eq(tst.bias, torch.zeros(5))
tst = nn.BatchNorm2d(5)
init = [tst.weight.clone(), tst.bias.clone()]
cond_init(tst, func = lambda x: x.data.fill_(1.))
test_eq(tst.weight, init[0])
test_eq(tst.bias, init[1])apply_leaf
apply_leaf (m, f)
将 f 应用于 m 的子模块。
tst = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(4,5), nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(4,5), nn.Linear(4,5)))
apply_leaf(tst, partial(init_default, func=lambda x: x.data.fill_(1.)))
for l in [tst[0], *tst[1]]: test_eq(l.weight, torch.ones(5,4))
for l in [tst[0], *tst[1]]: test_eq(l.bias, torch.zeros(5))apply_init
apply_init (m, func=<function kaiming_normal_>)
使用 func 初始化 m 的所有非 batchnorm 层。
tst = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(4,5), nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(4,5), nn.BatchNorm1d(5)))
init = [tst[1][1].weight.clone(), tst[1][1].bias.clone()]
apply_init(tst, func=lambda x: x.data.fill_(1.))
for l in [tst[0], tst[1][0]]: test_eq(l.weight, torch.ones(5,4))
for l in [tst[0], tst[1][0]]: test_eq(l.bias, torch.zeros(5))
test_eq(tst[1][1].weight, init[0])
test_eq(tst[1][1].bias, init[1])autograd jit 函数
script_use_ctx
script_use_ctx (f)
装饰器:创建 jit 脚本并在 *args 之后将 ctx.saved_variables 中的所有内容传递给 f
script_save_ctx
script_save_ctx (static, *argidx)
装饰器:创建 jit 脚本并使用 ctx.save_for_backward 保存索引为 argidx 的参数
script_fwd
script_fwd (*argidx)
装饰器:创建静态 jit 脚本并使用 ctx.save_for_backward 保存索引为 argidx 的参数
script_bwd
script_bwd (f)
装饰器:创建静态 jit 脚本并在 *args 之后将 ctx.saved_variables 中的所有内容传递给 f
grad_module
grad_module (cls)
装饰器:将 cls 转换为一个 autograd 函数
ismin_torch
ismin_torch (min_version)
使用 packaging.version 检查 torch.__version__ 是否 >= min_version
notmax_torch
notmax_torch (max_version)
使用 packaging.version 检查 torch.__version__ 是否 < max_version