tst = CrossEntropyLossFlat(reduction='none')
output = torch.randn(32, 5, 10)
target = torch.randint(0, 10, (32,5))
#nn.CrossEntropy would fail with those two tensors, but not our flattened version.
_ = tst(output, target)
test_fail(lambda x: nn.CrossEntropyLoss()(output,target))
#Associated activation is softmax
test_eq(tst.activation(output), F.softmax(output, dim=-1))
#This loss function has a decodes which is argmax
test_eq(tst.decodes(output), output.argmax(dim=-1))损失函数
BaseLoss
BaseLoss (loss_cls, *args, axis:int=-1, flatten:bool=True, floatify:bool=False, is_2d:bool=True, **kwargs)
与 loss_cls 相同,但会展平输入和目标。
| 类型 | 默认值 | 详情 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| loss_cls | 未初始化的 PyTorch 兼容损失函数 | ||
| args | VAR_POSITIONAL | ||
| axis | int | -1 | 类别轴 |
| flatten | bool | True | 在计算损失之前展平 inp 和 targ |
| floatify | bool | False | 将 targ 转换为 float 类型 |
| is_2d | bool | True | 应用 flatten 时是否保留一个或两个通道 |
| kwargs | VAR_KEYWORD |
将通用损失函数封装在 BaseLoss 中可以为你的损失函数提供额外的功能
- 在计算损失之前展平张量,因为它更方便(可能会进行转置将
axis放在最后) - 一个可选的
activation方法,用于告知库损失函数中是否融合了激活函数(对于推理和诸如Learner.get_preds或Learner.predict之类的方法很有用) - 一个可选的
decodes方法,用于在推理时对预测进行解码(例如,分类中的 argmax)
args 和 kwargs 将在初始化时传递给 loss_cls 以实例化损失函数。对于像 softmax 这样通常在最后一个轴上执行的损失函数,axis 会被放在最后。如果 floatify=True,targs 将被转换为浮点数(对于只接受浮点数目标的损失函数,如 BCEWithLogitsLoss 很有用),并且 is_2d 决定了我们在展平输入时是保留第一个维度(批量大小)还是完全展平。对于像交叉熵这样的损失函数,我们希望保留第一个维度,而对于几乎所有其他损失函数,我们希望完全展平。
CrossEntropyLossFlat
CrossEntropyLossFlat (*args, axis:int=-1, weight=None, ignore_index=-100, reduction='mean', flatten:bool=True, floatify:bool=False, is_2d:bool=True)
与 nn.CrossEntropyLoss 相同,但会展平输入和目标。
| 类型 | 默认值 | 详情 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| args | VAR_POSITIONAL | ||
| axis | int | -1 | 类别轴 |
| weight | NoneType | None | |
| ignore_index | int | -100 | |
| reduction | str | mean | |
| flatten | bool | True | |
| floatify | bool | False | |
| is_2d | bool | True |
#In a segmentation task, we want to take the softmax over the channel dimension
tst = CrossEntropyLossFlat(axis=1)
output = torch.randn(32, 5, 128, 128)
target = torch.randint(0, 5, (32, 128, 128))
_ = tst(output, target)
test_eq(tst.activation(output), F.softmax(output, dim=1))
test_eq(tst.decodes(output), output.argmax(dim=1))Focal Loss 与交叉熵相似,只是在损失计算中降低了易于分类样本的权重。权重降低的强度与 gamma 参数的大小成正比。换句话说,gamma 越大,易于分类的样本对损失的贡献越小。
FocalLossFlat
FocalLossFlat (*args, gamma:float=2.0, axis:int=-1, weight=None, reduction='mean', **kwargs)
与 CrossEntropyLossFlat 相同,但增加了焦点参数 gamma。Focal Loss 由 Lin 等人引入,论文链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1708.02002.pdf。请注意,论文中的类别加权因子 alpha 可以通过传递给 F.cross_entropy 的 PyTorch weight 参数来实现。
| 类型 | 默认值 | 详情 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| args | VAR_POSITIONAL | ||
| gamma | float | 2.0 | 焦点参数。值越高,降低易于分类样本对损失的贡献越大。 |
| axis | int | -1 | 类别轴 |
| weight | NoneType | None | |
| reduction | str | mean | |
| kwargs | VAR_KEYWORD |
FocalLoss
FocalLoss (gamma:float=2.0, weight:Tensor=None, reduction:str='mean')
与 nn.Module 相同,但子类无需调用 super().__init__
| 类型 | 默认值 | 详情 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| gamma | float | 2.0 | 焦点参数。值越高,降低易于分类样本对损失的贡献越大。 |
| weight | Tensor | None | 手动为每个类别分配的缩放权重 |
| reduction | str | mean | 应用于输出的 PyTorch 归约(reduction)方法 |
#Compare focal loss with gamma = 0 to cross entropy
fl = FocalLossFlat(gamma=0)
ce = CrossEntropyLossFlat()
output = torch.randn(32, 5, 10)
target = torch.randint(0, 10, (32,5))
test_close(fl(output, target), ce(output, target))
#Test focal loss with gamma > 0 is different than cross entropy
fl = FocalLossFlat(gamma=2)
test_ne(fl(output, target), ce(output, target))#In a segmentation task, we want to take the softmax over the channel dimension
fl = FocalLossFlat(gamma=0, axis=1)
ce = CrossEntropyLossFlat(axis=1)
output = torch.randn(32, 5, 128, 128)
target = torch.randint(0, 5, (32, 128, 128))
test_close(fl(output, target), ce(output, target), eps=1e-4)
test_eq(fl.activation(output), F.softmax(output, dim=1))
test_eq(fl.decodes(output), output.argmax(dim=1))BCEWithLogitsLossFlat
BCEWithLogitsLossFlat (*args, axis:int=-1, floatify:bool=True, thresh:float=0.5, weight=None, reduction='mean', pos_weight=None, flatten:bool=True, is_2d:bool=True)
与 nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss 相同,但会展平输入和目标。
| 类型 | 默认值 | 详情 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| args | VAR_POSITIONAL | ||
| axis | int | -1 | 类别轴 |
| floatify | bool | True | 将 targ 转换为 float 类型 |
| thresh | float | 0.5 | 用于预测的阈值 |
| weight | NoneType | None | |
| reduction | str | mean | |
| pos_weight | NoneType | None | |
| flatten | bool | True | |
| is_2d | bool | True |
tst = BCEWithLogitsLossFlat()
output = torch.randn(32, 5, 10)
target = torch.randn(32, 5, 10)
#nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss would fail with those two tensors, but not our flattened version.
_ = tst(output, target)
test_fail(lambda x: nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()(output,target))
output = torch.randn(32, 5)
target = torch.randint(0,2,(32, 5))
#nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss would fail with int targets but not our flattened version.
_ = tst(output, target)
test_fail(lambda x: nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()(output,target))
tst = BCEWithLogitsLossFlat(pos_weight=torch.ones(10))
output = torch.randn(32, 5, 10)
target = torch.randn(32, 5, 10)
_ = tst(output, target)
test_fail(lambda x: nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()(output,target))
#Associated activation is sigmoid
test_eq(tst.activation(output), torch.sigmoid(output))BCELossFlat
BCELossFlat (*args, axis:int=-1, floatify:bool=True, weight=None, reduction='mean')
与 nn.BCELoss 相同,但会展平输入和目标。
| 类型 | 默认值 | 详情 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| args | VAR_POSITIONAL | ||
| axis | int | -1 | 类别轴 |
| floatify | bool | True | 将 targ 转换为 float 类型 |
| weight | NoneType | None | |
| reduction | str | mean |
tst = BCELossFlat()
output = torch.sigmoid(torch.randn(32, 5, 10))
target = torch.randint(0,2,(32, 5, 10))
_ = tst(output, target)
test_fail(lambda x: nn.BCELoss()(output,target))MSELossFlat
MSELossFlat (*args, axis:int=-1, floatify:bool=True, reduction='mean')
与 nn.MSELoss 相同,但会展平输入和目标。
| 类型 | 默认值 | 详情 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| args | VAR_POSITIONAL | ||
| axis | int | -1 | 类别轴 |
| floatify | bool | True | 将 targ 转换为 float 类型 |
| reduction | str | mean |
tst = MSELossFlat()
output = torch.sigmoid(torch.randn(32, 5, 10))
target = torch.randint(0,2,(32, 5, 10))
_ = tst(output, target)
test_fail(lambda x: nn.MSELoss()(output,target))L1LossFlat
L1LossFlat (*args, axis=-1, floatify=True, reduction='mean')
与 nn.L1Loss 相同,但会展平输入和目标。
| 类型 | 默认值 | 详情 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| args | VAR_POSITIONAL | ||
| axis | int | -1 | 类别轴 |
| floatify | bool | True | 将 targ 转换为 float 类型 |
| reduction | str | mean |
LabelSmoothingCrossEntropy
LabelSmoothingCrossEntropy (eps:float=0.1, weight:Tensor=None, reduction:str='mean')
与 nn.Module 相同,但子类无需调用 super().__init__
| 类型 | 默认值 | 详情 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| eps | float | 0.1 | 插值公式的权重 |
| weight | Tensor | None | 手动为每个类别分配的缩放权重,传递给 F.nll_loss |
| reduction | str | mean | 应用于输出的 PyTorch 归约(reduction)方法 |
lmce = LabelSmoothingCrossEntropy()
output = torch.randn(32, 5, 10)
target = torch.randint(0, 10, (32,5))
test_close(lmce(output.flatten(0,1), target.flatten()), lmce(output.transpose(-1,-2), target))在我们定义的公式之上,我们还定义
- 一个
reduction属性,在调用Learner.get_preds时使用 - 传递给 BCE 的
weight属性。 - 一个
activation函数,表示损失函数中融合的激活函数(因为我们幕后使用了交叉熵)。在调用Learner.get_preds或Learner.predict时,它将被应用于模型的输出。 - 一个
decodes函数,将模型的输出转换为与目标类似的格式(此处为索引)。这用于Learner.predict和Learner.show_results中对预测进行解码。
LabelSmoothingCrossEntropyFlat
LabelSmoothingCrossEntropyFlat (*args, axis:int=-1, eps=0.1, reduction='mean', flatten:bool=True, floatify:bool=False, is_2d:bool=True)
与 LabelSmoothingCrossEntropy 相同,但会展平输入和目标。
| 类型 | 默认值 | 详情 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| args | VAR_POSITIONAL | ||
| axis | int | -1 | 类别轴 |
| eps | float | 0.1 | |
| reduction | str | mean | |
| flatten | bool | True | |
| floatify | bool | False | |
| is_2d | bool | True |
#These two should always equal each other since the Flat version is just passing data through
lmce = LabelSmoothingCrossEntropy()
lmce_flat = LabelSmoothingCrossEntropyFlat()
output = torch.randn(32, 5, 10)
target = torch.randint(0, 10, (32,5))
test_close(lmce(output.transpose(-1,-2), target), lmce_flat(output,target))我们提供了一个通用的 Dice 损失函数,用于分割任务。在 Kaggle 竞赛中,它通常与 CrossEntropyLoss 或 FocalLoss 一起使用。这与 DiceMulti 指标非常相似,但为了能够进行求导,我们将 argmax 激活函数替换为 softmax,并将其与独热编码的目标掩码进行比较。此函数还添加了一个 smooth 参数,以帮助提高 IoU (Intersection over Union) 除法中的数值稳定性。如果你的网络在使用此 DiceLoss 时学习困难,可以尝试将 DiceLoss 构造函数中的 square_in_union 参数设置为 True。
DiceLoss
DiceLoss (axis:int=1, smooth:float=1e-06, reduction:str='sum', square_in_union:bool=False)
用于分割的 Dice Loss
| 类型 | 默认值 | 详情 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| axis | int | 1 | 类别轴 |
| smooth | float | 1e-06 | 帮助提高 IoU 除法中的数值稳定性 |
| reduction | str | sum | 应用于输出的 PyTorch 归约(reduction)方法 |
| square_in_union | bool | False | 对预测值进行平方以增加梯度斜率 |
dl = DiceLoss()
_x = tensor( [[[1, 0, 2],
[2, 2, 1]]])
_one_hot_x = tensor([[[[0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0]],
[[1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1]],
[[0, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 0]]]])
test_eq(dl._one_hot(_x, 3), _one_hot_x)dl = DiceLoss()
model_output = tensor([[[[2., 1.],
[1., 5.]],
[[1, 2.],
[3., 1.]],
[[3., 0],
[4., 3.]]]])
target = tensor([[[2, 1],
[2, 0]]])
dl_out = dl(model_output, target)
test_eq(dl.decodes(model_output), target)dl = DiceLoss(reduction="mean")
#identical masks
model_output = tensor([[[.1], [.1], [100.]]])
target = tensor([[2]])
test_close(dl(model_output, target), 0)
#50% intersection
model_output = tensor([[[.1, 100.], [.1, .1], [100., .1]]])
target = tensor([[2, 1]])
test_close(dl(model_output, target), .66, eps=0.01)作为 Dice Loss 的测试用例,考虑卫星图像分割。假设我们有三个类别:背景 (0)、河流 (1) 和道路 (2)。我们来看一个具体的目标
target = torch.zeros(100,100)
target[:,5] = 1
target[:,50] = 2
plt.imshow(target);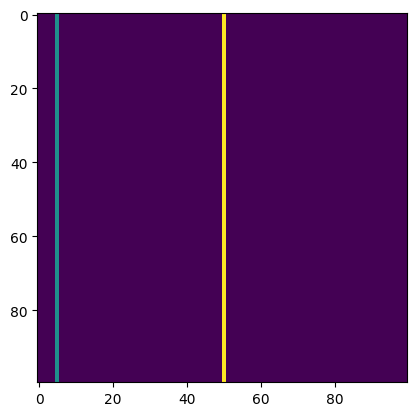
在这个例子中,几乎所有内容都是背景,图像左侧有一条细长的河流,图像中间有一条细长的道路。如果所有数据都与此相似,我们称之为类别不平衡,意味着某些类别(如河流和道路)出现频率相对较低。如果我们的模型仅预测所有像素都是“背景”(即值为 0),那么它对大多数像素的预测是正确的。但这将是一个糟糕的模型,Dice Loss 应该反映出这一点
model_output_all_background = torch.zeros(3, 100,100)
# assign probability 1 to class 0 everywhere
# to get probability 1, we just need a high model output before softmax gets applied
model_output_all_background[0,:,:] = 100# add a batch dimension
model_output_all_background = torch.unsqueeze(model_output_all_background,0)
target = torch.unsqueeze(target,0)在这里,我们的 Dice Score 应该约为 1/3,因为“背景”类别被正确预测(几乎所有像素都是如此),但其他两个类别从未被正确预测。Dice Score 为 1/3 意味着 Dice Loss 为 1 - 1/3 = 2/3
test_close(dl(model_output_all_background, target), 0.67, eps=0.01)如果模型能正确预测所有内容,Dice Loss 应该为零
correct_model_output = torch.zeros(3, 100,100)
correct_model_output[0,:,:] = 100
correct_model_output[0,:,5] = 0
correct_model_output[0,:,50] = 0
correct_model_output[1,:,5] = 100
correct_model_output[2,:,50] = 100
correct_model_output = torch.unsqueeze(correct_model_output, 0)test_close(dl(correct_model_output, target), 0)你可以轻松地将此损失函数与 FocalLoss 结合,定义一个 CombinedLoss,以平衡目标掩码上的全局特征 (Dice) 和局部特征 (Focal)。
class CombinedLoss:
"Dice and Focal combined"
def __init__(self, axis=1, smooth=1., alpha=1.):
store_attr()
self.focal_loss = FocalLossFlat(axis=axis)
self.dice_loss = DiceLoss(axis, smooth)
def __call__(self, pred, targ):
return self.focal_loss(pred, targ) + self.alpha * self.dice_loss(pred, targ)
def decodes(self, x): return x.argmax(dim=self.axis)
def activation(self, x): return F.softmax(x, dim=self.axis)cl = CombinedLoss()
output = torch.randn(32, 4, 5, 10)
target = torch.randint(0,2,(32, 5, 10))
_ = cl(output, target)# Tests to catch future changes to pickle which cause some loss functions to be 'unpicklable'.
# This causes problems with `Learner.export` as the model can't be pickled with these particular loss funcitons.
losses_picklable = [
(BCELossFlat(), True),
(BCEWithLogitsLossFlat(), True),
(CombinedLoss(), True),
(CrossEntropyLossFlat(), True),
(DiceLoss(), True),
(FocalLoss(), True),
(FocalLossFlat(), True),
(L1LossFlat(), True),
(LabelSmoothingCrossEntropyFlat(), True),
(LabelSmoothingCrossEntropy(), True),
(MSELossFlat(), True),
]
for loss, picklable in losses_picklable:
try:
pickle.dumps(loss, protocol=2)
except (pickle.PicklingError, TypeError) as e:
if picklable:
# Loss was previously picklable but isn't currently
raise e